The situation is equivalent with the relative risk;A value lower than 100 indicates decreased risk The 95% confidence intervals and statistical95% confidence interval (CI), 073–148)

Assessing Heterogeneity Of Treatment Effect Estimating Patient Specific Efficacy And Studying Variation In Odds Ratios Risk Ratios And Risk Differences Statistical Thinking
Why is relative risk better than odds ratio
Why is relative risk better than odds ratio-Odds ratios (OR) are commonly reported in the medical literature as the measure of association between exposure and outcome However, it is relative risk that people more intuitively understand as a measure of association Relative risk can be directly determined in a cohort study by calculating a risk ratio (RR) The odds ratio can be confused with relative risk As stated above, the odds ratio is a ratio of 2 odds As odds of an event are always positive, the odds ratio is always positive and ranges from zero to very large The relative risk is a ratio of probabilities of the event occurring in all exposed individuals versus the event occurring in all nonexposed individuals



Q Tbn And9gcqsrft9mxr7dpz7nmjrd2rigdx Ivp6aahq2v9iti13quuix7yw Usqp Cau
Confidence Intervals Several methods for computing confidence intervals for proportion difference, proportion ratio, and odds ratio have been proposed We now show the methods that are available in NCSS Difference Four methods are available for computing a confidence interval of the difference between the two proportions ∆=P 1 −P 2Odds ratios, relative risk, and β0 from the logit model are presented Keywords st0041, cc, cci, cs, csi, logistic, logit, relative risk, case–control study, odds ratio, cohort study 1 Background Popular methods used to analyze binary response data include the probit model, discriminant analysis, and logistic regressionThe Odds Ratio (OR) is 15 and the 95% CI ((1α) =095) is (, ) The Absolute Risk Reduction (ARR) is 01 and the 95% CI is (0045, ) The Relative Risk Reduction (RRR) is 025 and the 95% CI is (, ) The Number of Needed Treat (NNT) is 10 and the 95% CI is (4976, )
Confidence Intervals for Risk Ratios and Odds Ratios You are already familiar with risk ratios and odds ratios Risk ratio RR = CI e /CI u where CI e =cumulative incidence in exposed (index) group and CI u = cumulative incidence in the unexposed (reference) group Odds ratio OR = (odds of disease in exposed) / (odds of disease in unexposed) Both RR and OR are estimates from samples, and they are continuous measuresAs an extreme example of the difference between risk ratio and odds ratio, if action A carries a risk of a negative outcome of 999% while action B has a risk of 990% the relative risk is approximately 1 while the odds ratio between A and B is 10 (1% = An odds ratio of above 1 means that there is a greater likelihood of having the outcome and an Odds ratio of below 1 means that there is a lesser likelihood of having the outcome Simple enough up to now?
In the above example, after the odds ratio is corrected (where OR=327 and P 0 =024), the risk ratio becomes 212 (95% confidence interval, ), ie, very low birthweight neonates in Hospital A had twice the risk of neonatal death than those in Hospital B The study reports that patients with a prolonged electrocardiographic QTc interval were more likely to die within 90 days compared with patients without a prolonged interval (relative risk RR=25;If the confidence interval contains the relative risk of 100, the result is not significant It would then have to be examined whether the confidence interval for the relative risk is completely under 100 (= protective effect) or completely above it (= increase in risk)



Www Annalsthoracicsurgery Org Article S0003 4975 07 009 3 Pdf




Iv Estimate And Interpret The Relative Risk Chegg Com
The relative risk (RR) and the odds ratio (OR) are the two most widely used measures of association in epidemiology a commonly used method of computing confidence intervals for relative riskThe odds ratio for lettuce was calculated to be 112 How would you interpret the odds ratio? The odds ratio will be greater than the relative risk if the relative risk is greater than one and less than the relative risk otherwise In the example above, if the adjusted odds ratio were interpreted as a relative risk, it would suggest that the risk of antibiotic associated diarrhoea is reduced by 75% for the intervention relative to the placebo group




Simple Way To Visualise Odds Ratios In R Stack Overflow




Ci For Or And Rr Relative Risk Odds Ratio
B Confidence Intervals for the Risk Ratio (Relative Risk) The risk difference quantifies the absolute difference in risk or prevalence, whereas the relative risk is, as the name indicates, a relative measure Both measures are useful, but they give different perspectives on the information A cumulative incidence is a proportion that provides a measure of risk, and a relative risk (or risk ratio) is computed by taking the ratio The odds ratio is reported as 1 with a confidence interval of (144, 234) Like we did with relative risk, we could look at the lower boundary and make a statement such as "the odds of MI are at least 44% higher for subjects taking placebo than for subjects taking aspirin" Or we might say "the estimated odds of MI were % higher for the placebo group" You may have noticed that the odds ratio and relative riskReporting Odds Ratio The odds ratio comparing death rates after the standard treatment to the new treatment was OR 3 suggesting that those on the control treatment are more likely to die As with the relative risk, the odds ratio is said to be significant if the confidence interval




Assessing Heterogeneity Of Treatment Effect Estimating Patient Specific Efficacy And Studying Variation In Odds Ratios Risk Ratios And Risk Differences Statistical Thinking



Http Www Sjsu Edu Faculty Gerstman Hs267 Exam Examples Pdf
Sometimes, we see the log odds ratio instead of the odds ratio The log OR comparing women to men is log(144) = 036 The log OR comparing men to women is log(069) = 036 log OR > 0 increased risk log OR = 0 no difference in risk log OR < 0 decreased risk Odds Ratio 0 5 10 15 More on the Odds Ratio Log Odds Ratio4 2 0 2 4Relative Risk is the ratio of incidence of disease in Exposed group to that in Nonexposed group from a cohort/prospective study If Relative Risk is larger than 1, (1α)% confidence interval b) The Attributable Risk and the corresponding 100(1α)% confidence interval Thus, the 95% CI is the interval of values in which the true risk ratio is likely to lie with a probability of 95% To be statistically significant with a P




Delta Method Standard Errors R Bloggers



Academic Oup Com Aje Article Pdf 171 5 618 Kwp440 Pdf
When the Odds ratio is above 1 and below 2, the likelihood of having the event is represented as XX % higher odds (where XX % is Odds ratio 1) That means that if odds ratioConfidence interval for odds ratio Odds ratio of having disease for sector 1 vs sector 2 SECTOR * DISEASE Crosstabulation Count 22 95 117 35 44 79 57 139 196 Sector 1 (X=1) Sector 2 (X=2) SECTOR Total Yes (Y=1) No (Y=2) DISEASE Total Figure (d) Contingency Table Risk Estimate291 153 270 666 1458 1176 1808 196 Odds Ratio for SECTOR (Sector 1Population attributable risk is presented as a percentage with a confidence interval when the odds ratio is greater than or equal to one (Sahai and Kurshid, 1996) Technical validation A confidence interval (CI) for the odds ratio is calculated using an exact conditional likelihood method ( Martin and Austin, 1991 )




Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Youtube
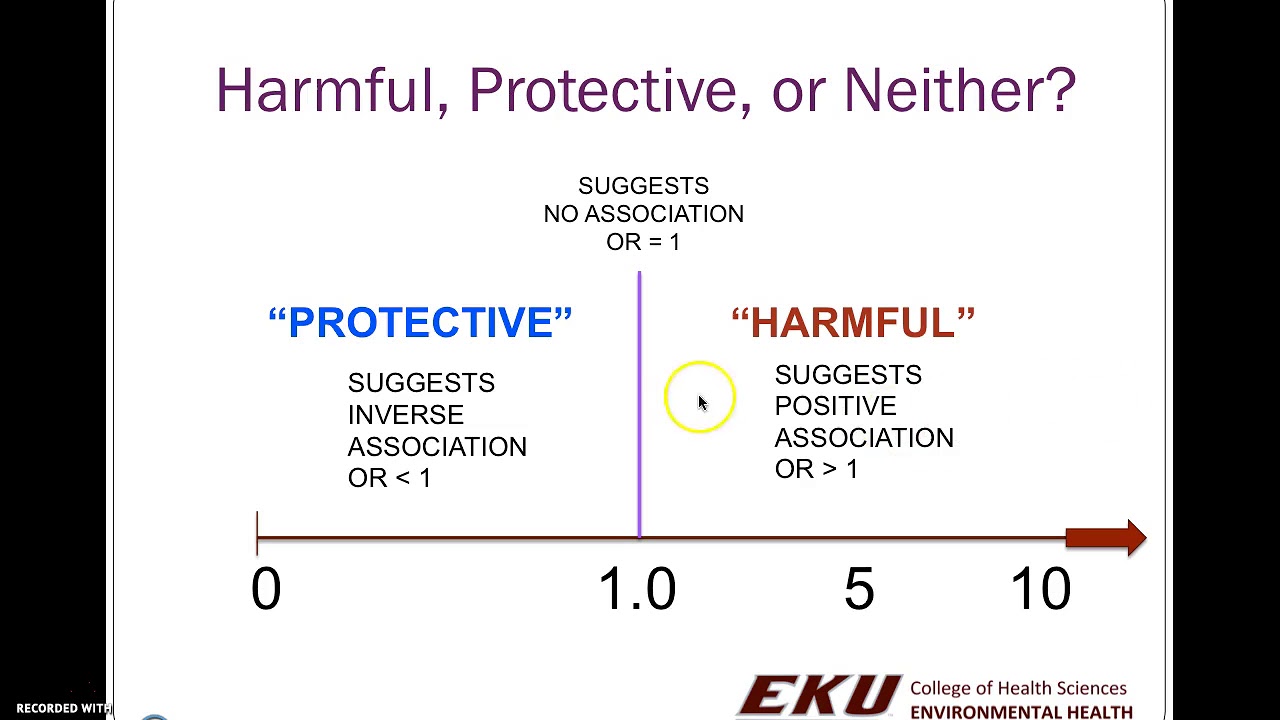



Part 1 Of 3 Interpreting Odds Risk And Rate Ratio Results With 95 Ci Youtube
A confidence interval for the MantelHaenszel odds ratio in StatsDirect is calculated using the Robins, Breslow and Greenland variance formula (Robins et al, 1986) or by the method of Sato (1990) if the estimate of the odds ratio can not be determined A chisquare test statistic is given with its associated probability that the pooled oddsIf the confidence interval does not cross the line of no difference than the observed difference is statistically significant, because you know it is highly unlikely that the two groups are the same For both relative risk (RR) and odds ratio (OR), the "line of no difference" is 1 So an RR or OR of 1 means there is no difference betweenAtive risk (the ratio of two proportions), and the odds ratio The risk difference is an absolute measurement of effect, while the relative risk and the odds ratio are relative measurements for comparing outcomes In retrospective casecontrol studies, the odds ratio is used because the other two parameters cannot be estimated




Calculation And Interpretation Of Odds Ratio Or And Risk Ratio Rr Youtube
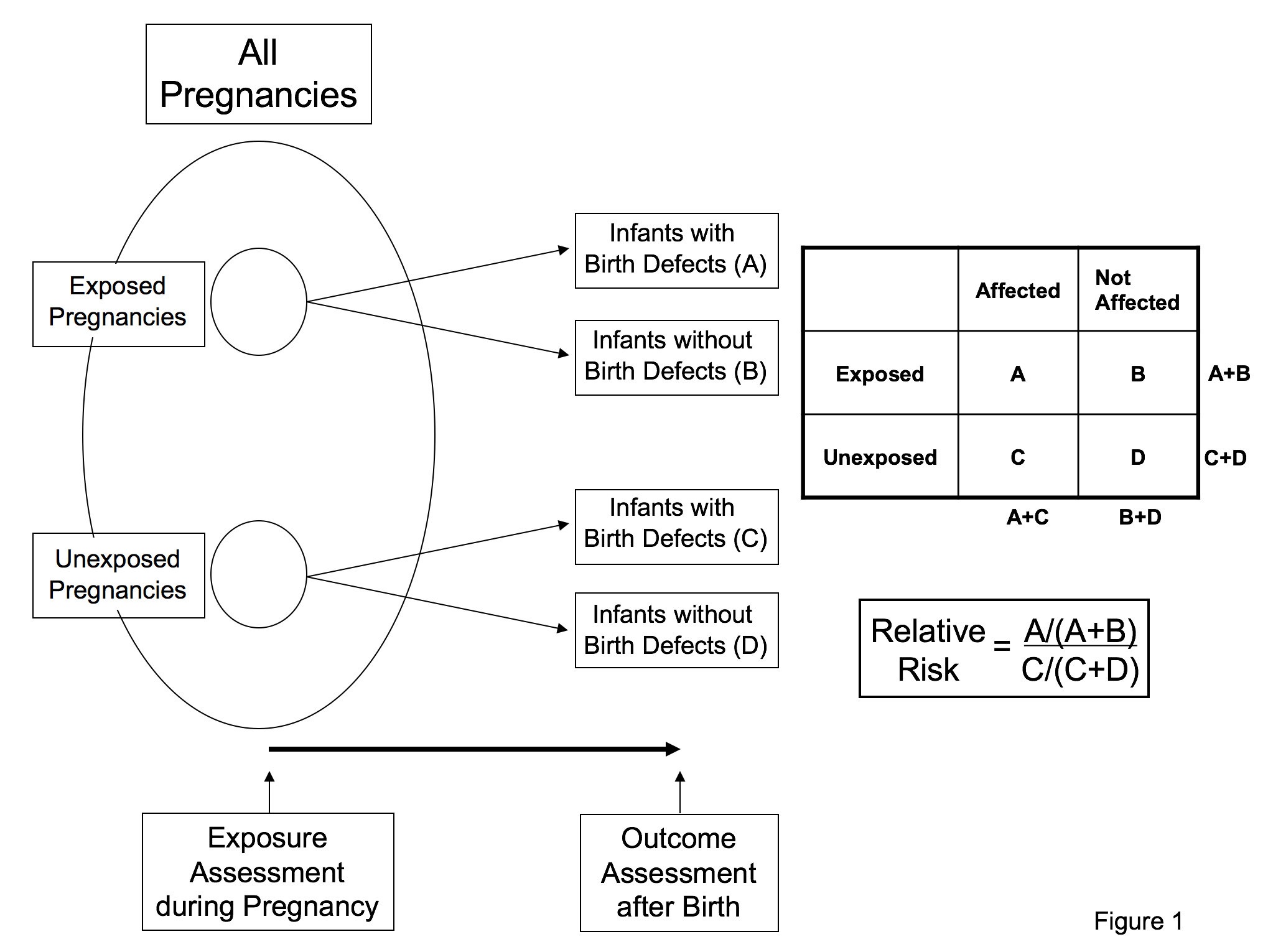



Society For Birth Defects Research And Prevention
2x2 Contingency Table with Odds Ratios, etc ·Rates, Risk Ratio, Odds, Odds Ratio, Log Odds ·Phi Coefficient of Association ·ChiSquare Test of Association ·Fisher Exact Probability Test For two groups of subjects, each sorted according to the absence or presence of some particular characteristic or condition, this page will calculateThe problem of constructing better confidence intervals for the risk ratio from a 2x2 table has a long history and is been considered by many authors Related problem of confidence interval for the odds ratio and difference of risks are also beenAn odds ratio of 112 means the odds of having eaten lettuce were 11 times higher among casepatients than controls Because the odds ratio is greater than 10, lettuce might be a risk factor for illness after the luncheon The magnitude of the odds ratio



Academic Oup Com Aje Article Pdf 151 5 531 151 5 531 Pdf




Data Analysis For The Bsc Year Ppt Download
Although the odds ratio is close to the relative risk when the outcome is relatively uncommon 12, there is a recognized problem that odds ratios do not give a good approximation of the relative risk when the initial risk is high 13, 14 Furthermore, an odds ratio will always exaggerate the size of the effect compared to a relative risk 15, 16 Odds ratio is similar to relative risk In the sheepskin trial the relative risk was 058 and the odds ratio was 054 For most clinical trials where the event rate is low, that is less than 10% of all participants have an event, the odds ratio and relative risk can be considered interchangeableAbout Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators
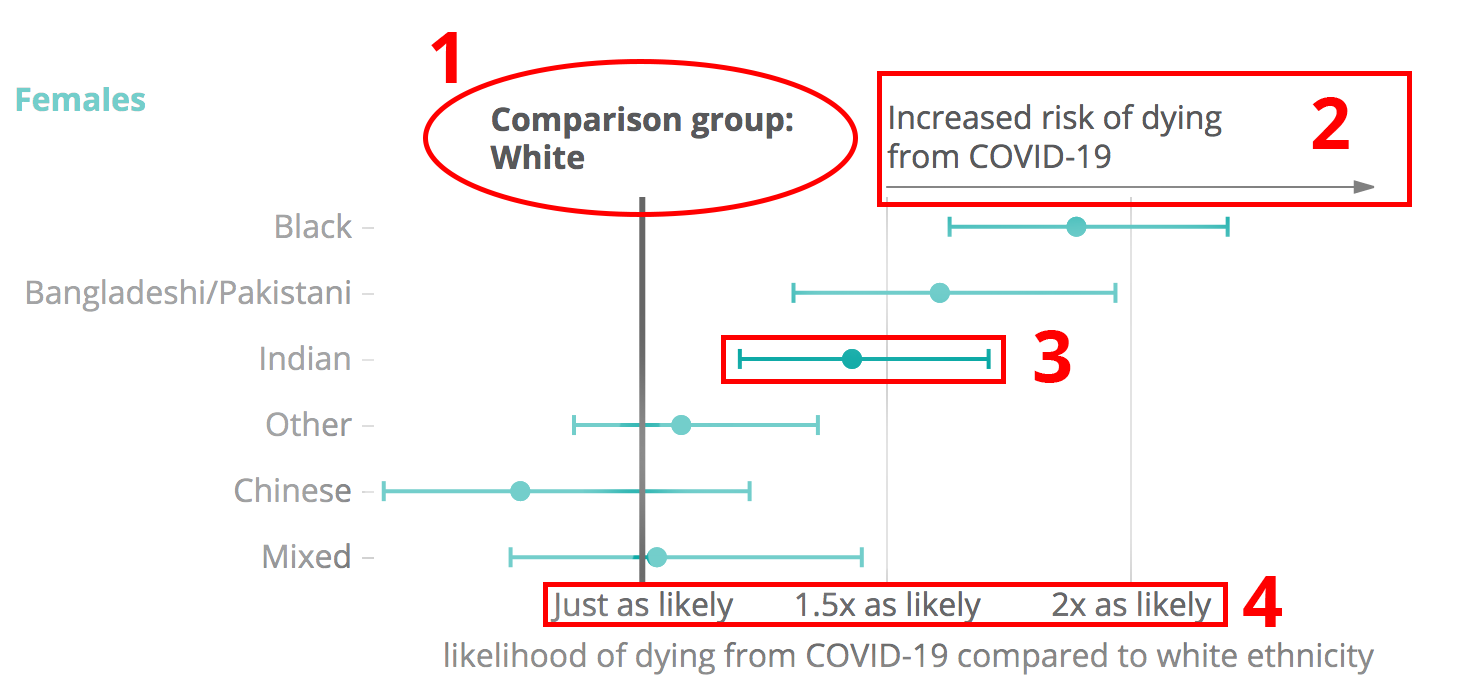



Against All Odds How To Visualise Odds Ratios To Non Expert Audiences Henry Lau




Odds Ratio Relative Risk Calculation Definition Probability Odds Youtube
95% confidence interval CI 1541) Having a confidence interval between 15 and 41 for the risk ratio indicates that patients with a prolonged QTc interval were 1541 times more likely to die in 90 days than those without a prolonged QTc interval Odds ratios (eform) By default, coefplot displays the results as they have been stored by the estimation command in e(b) These raw coefficients may not always be what you want to see For example, in case of a logit model, you may want to use the eform option to transform the raw log odds to odds ratiosThe risk ratio is also called the relative risk and the rate ratio, all of which can be conveniently abbreviated to RR Having calculated our estimate of effect, we would like a confidence interval for it Ratios are rather difficult things to deal with statistically Because risk ratio is a ratio, it has a very awkward distribution



Onlinelibrary Wiley Com Doi Pdf 10 1002 Sim



Research Statistics Basics Contents 1 Basic Concepts 2 References Basic Concepts Null Hypothesis The Hypothesis That The Independent Variable Has No Effect On The Dependent Variable For Example Steroids Do Not Improve Outcomes In Ards Would Be
You can also check your results with online calculator, like on statpagesorg, or Relative Risk and Risk Difference Confidence Intervals The latter explains how computations are done ( rr)) = 1 / a − 1 / ( a b) 1 / c − 1 / ( c d) (assuming a 2way crossclassification table, with a, b, c, and d denoting cell frequencies) Thus, the 95% CI is the interval of values in which the true risk ratio is likely to lie with a probability of 95% To be statistically significant with a PInterpreting confidence intervals for the odds ratio Interpreting confidence intervals for the odds ratio



Pdf A Method To Compute Multiplicity Corrected Confidence Intervals For Odds Ratios And Other Relative Effect Estimates



Www Teachepi Org Wp Content Uploads Oldte Documents Courses Fundamentals Pai Lecture4 Measures of effect and impact Pdf
Relative Risk (RR) & Odds Ratio (OR) Later in the chapter we will cover how confidence intervals are applied to RR & OR ERRATA At about the 300 mark the slide says "10,00" when it is really supposed to say "10,000" I added a pop up box to fix it Thanks to Mehdi Hedjazi for pointing this typo out in a youtube comment!In a control group The odds ratio (OR) is the odds of an event in an experimental group relative to that in a control group An RR or OR of 100 indicates that the risk is comparable in the two groups A value greater than 100 indicates increased risk;Approximation to the risk ratio since, in this case, 1−p1≈1−p2, so that ψ ≈ =φ − − = 2 1 2 2 1 1 1 1 p p p p p p Confidence Intervals for the Odds Ratio Many methods have been devised for computing confidence intervals for the odds ratio of two proportions 2 2 1 1 1 1 p p p p − − ψ= Eight of these methods are available in the
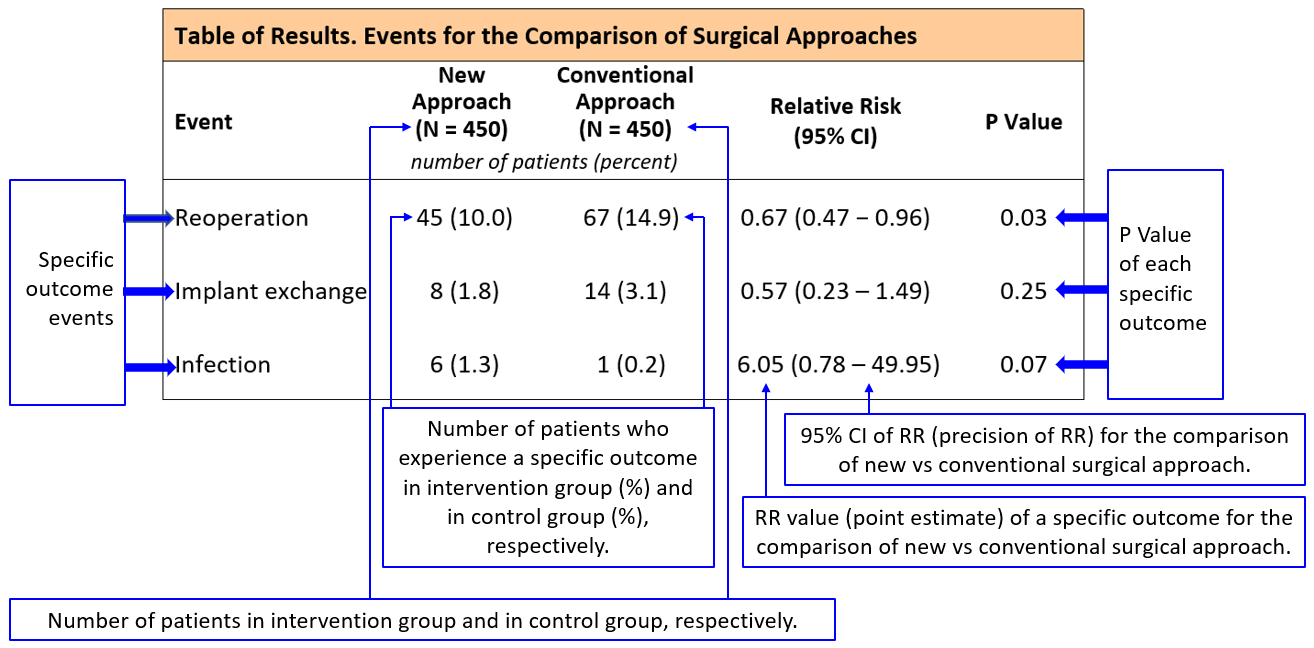



Interpreting Results From Randomized Trials




Questionable Utility Of The Relative Risk In Clinical Research A Call For Change To Practice Journal Of Clinical Epidemiology
Confidence Interval (CI) is the range of values that is likely to include the true population value and is used to measure the precision of the study's estimate (in this case, the precision of the Hazard Ratio) The narrower the confidence interval, the more precise the estimate (Precision will be affected by the study's sample size)Relative risk and 95% confidence intervals are more precise measures in comparison to odds ratios You can see that the underlying mathematics have yielded a different treatment effect from an odds ratio, RR = 357 (95% CI ) This comparison of actual risk ratios yields a stronger measure of association than odds ratios and helps They shouldn't be because they're actually interpreted differently So it's important to keep them separate and to be precise in the language you use The basic difference is that the odds ratio is a ratio of two odds (yep, it's that obvious) whereas the relative risk is a ratio of two probabilities



Understanding Mlogit Statahacks




Evidence Based Medicine American Academy Of Pediatrics
The most active quartile of women had a similar risk of breast cancer as the least active (odds ratio OR, 104; For pediatric arrest, the risk of survival if intubated during arrest was 411/1135 (36%) vs 460/1135 (41%) if not intubated Let's convert to odds and calculate an OR Intubated 411/ = 411/724 = 057 odds Nonintubated 460/ = 460/675 = 068 oddsThe risk ratio (or relative risk) is the ratio of the risk of an event in the two groups, whereas the odds ratio is the ratio of the odds of an event (see Box 92a ) For both measures a value of 1 indicates that the estimated effects are the same for both interventions Neither the risk ratio nor the odds ratio can be calculated for a study




Society For Birth Defects Research And Prevention
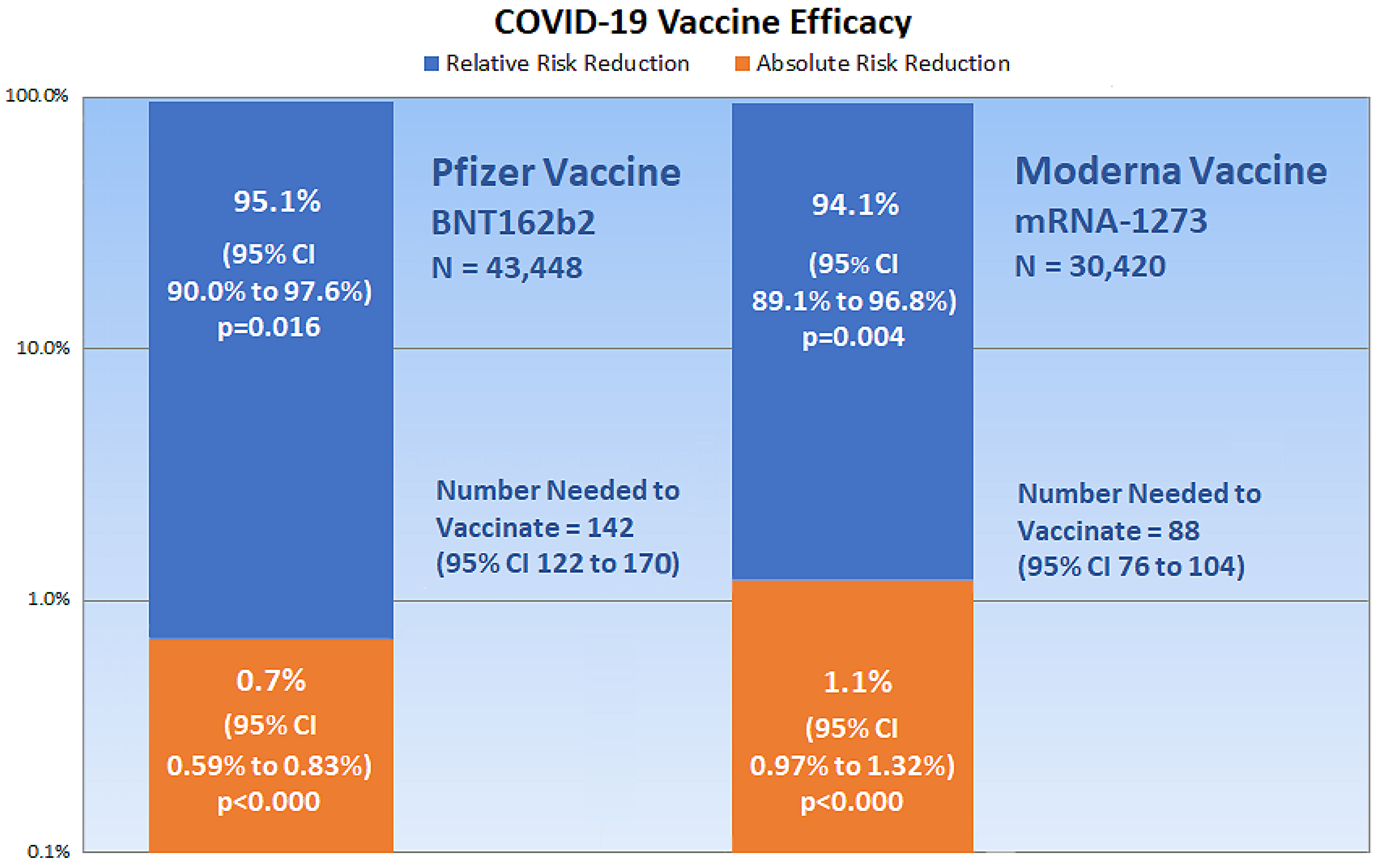



Medicina Free Full Text Outcome Reporting Bias In Covid 19 Mrna Vaccine Clinical Trials Html
In clinical studies, as well as in some other settings, the parameter of greatest interest is often the relative risk rather than the odds ratio The relative risk is best estimated using a population sample, but if the rare disease assumption holds, the odds ratio is a good approximation to the relative risk — the odds is p / (1 − p), so when p moves towards zero, 1 − p moves towards 1As an extreme example of the difference between risk ratio and odds ratio, if action A carries a risk of a negative outcome of 999% while action B has a risk of 990% the relative risk is approximately 1 while the odds associated with action A are more than 10 times higher than the odds in doing B (1% = 01% x 10, odds ratio calculation, relative risk calculation)




Empirical Confidence Interval Calibration For Population Level Effect Estimation Studies In Observational Healthcare Data Pnas



2



Q Tbn And9gcs4bcnrpynkp2cs4djpmsqpraxmoql9dbezlu6zyy V0zawzodp Usqp Cau




Assessing Confidence In The Results Of Network Meta Analysis Cinema Biorxiv



How To Read A Forest Plot Cochrane Uk
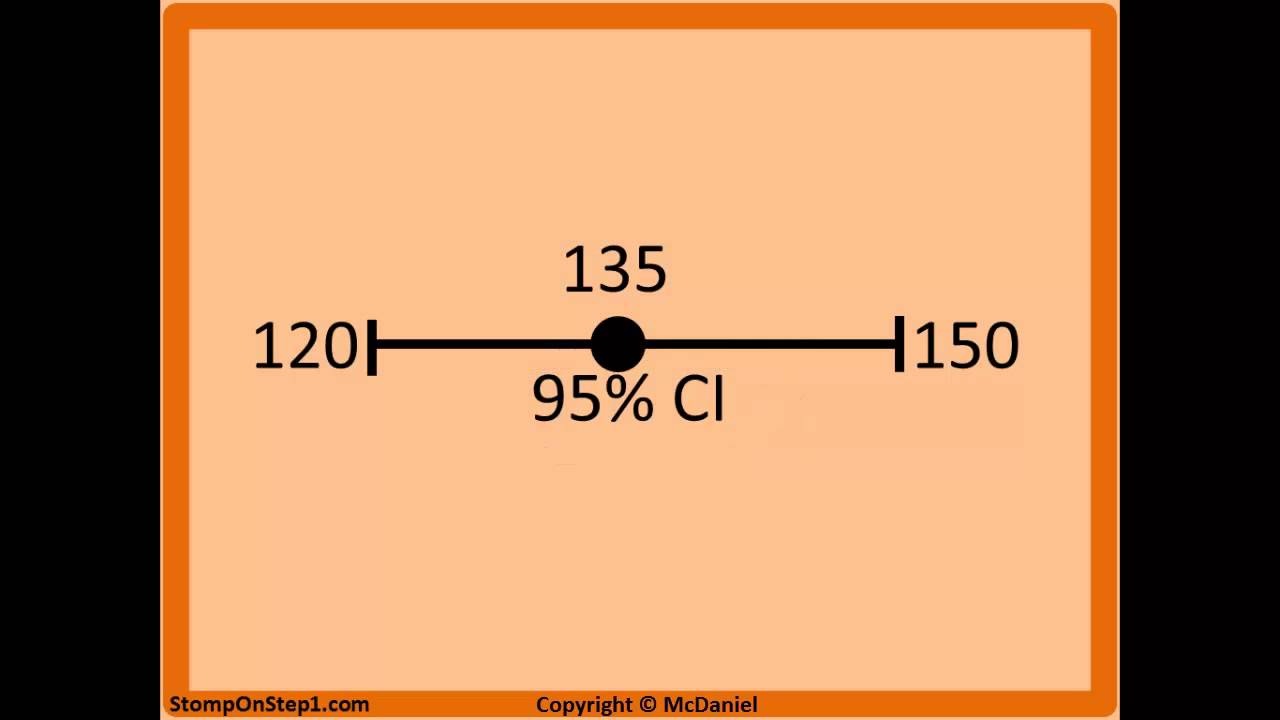



Confidence Interval Interpretation 95 Confidence Interval 90 99 Youtube




Statquest Odds Ratios And Log Odds Ratios Clearly Explained Youtube



Http Www Floppybunny Org Robin Web Virtualclassroom Stats Basics Part13 Risks Rates Odds Pdf




How To Create Odds Ratio And 95 Ci Plot In R Stack Overflow



Q Tbn And9gcqsrft9mxr7dpz7nmjrd2rigdx Ivp6aahq2v9iti13quuix7yw Usqp Cau




Effect Sizes Basicmedical Key




Questionable Utility Of The Relative Risk In Clinical Research A Call For Change To Practice Journal Of Clinical Epidemiology




Pdf A New Confidence Interval For Odds Ratio




Odds Ratios And Relative Risks Of T2d Diagnosis By Bmi Categories Download Scientific Diagram



Understanding Mlogit Statahacks
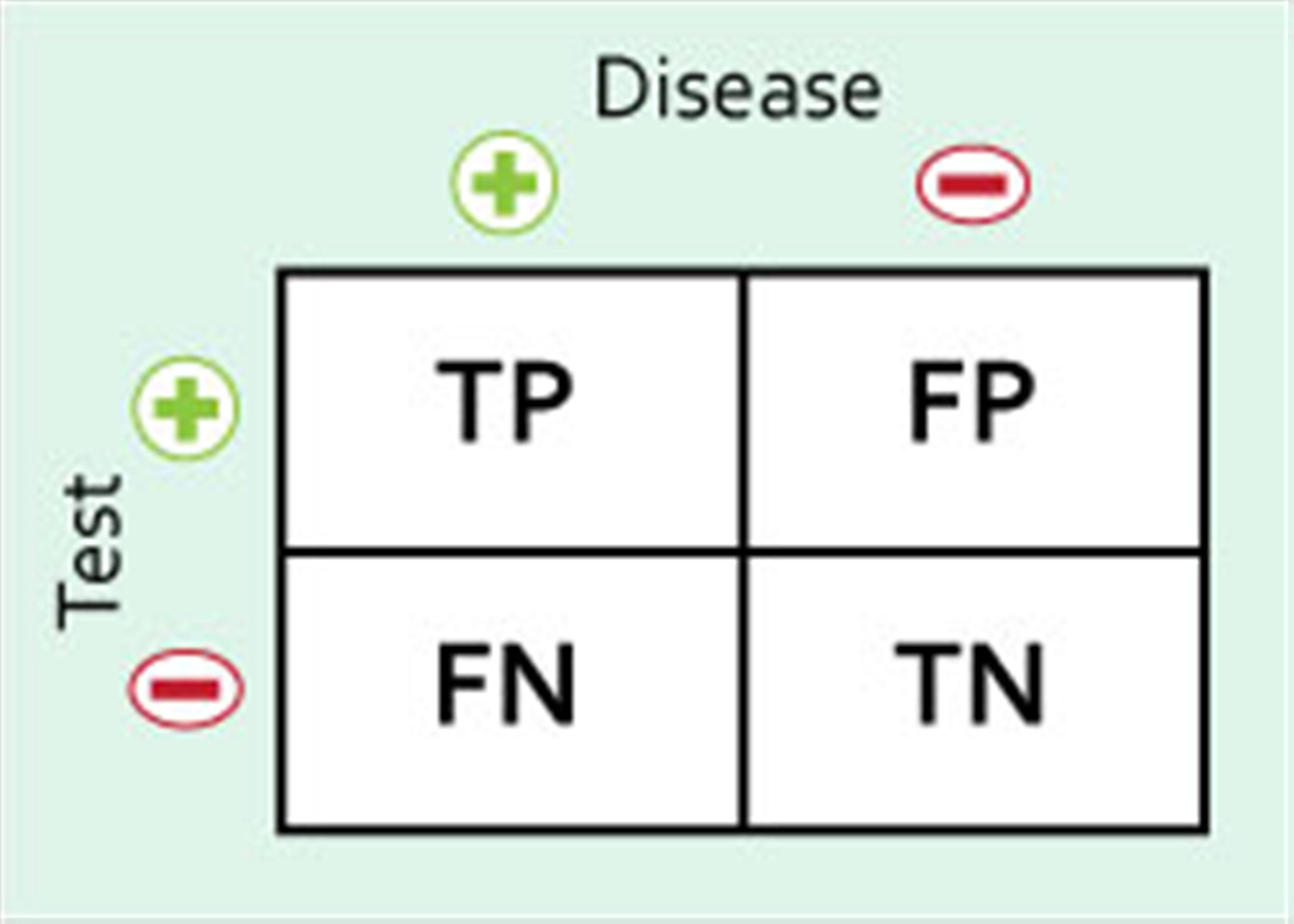



Statistic Definitions Basic Science Orthobullets



1




Effect Estimates And The Role Of The Chance Ppt Download
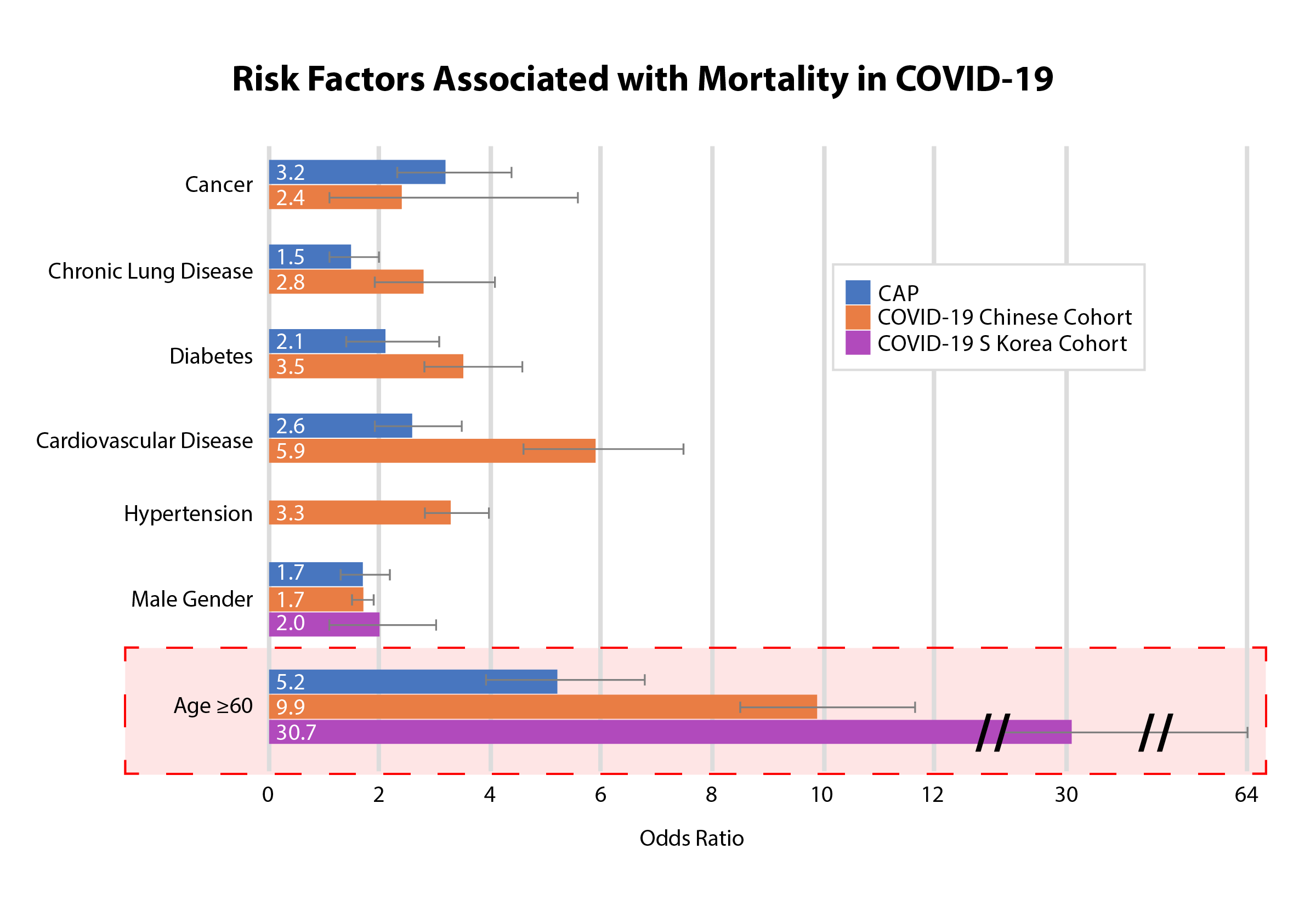



Nnt Review Odds Ratios Of Mortality Risk Factors




Risk Factors For Severe Illness And Death In Covid 19 A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis Medrxiv




Understanding Systematic Reviews And Meta Analysis Archives Of Disease In Childhood



2




Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios Youtube



Plos One Bleeding Risk With Long Term Low Dose Aspirin A Systematic Review Of Observational Studies




Delta Method Standard Errors R Bloggers




Odds Ratio Relative Risk Risk Difference Statistics Tutorial 30 Marinstatslectures Youtube




Effect Estimates And The Role Of The Chance Ppt Download




Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios



Training Cochrane Org Handbook Statistical Methods Revman5



Q Tbn And9gctxz8owky Sul84xtk4ggzacxwhkmhguhlxwyjj9avufagdrhwm Usqp Cau




Estimated Relative Risk Rr Compared With Odds Ratio Or For All Download Scientific Diagram




Prevalence And Relative Risk Odds Ratio Of Smoking According To Download Table




Linear Combinations Of Estimators Logistic Regression Coefficient Of Determination




How To Interpret And Use A Relative Risk And An Odds Ratio Youtube



Arxiv Org Pdf 1510
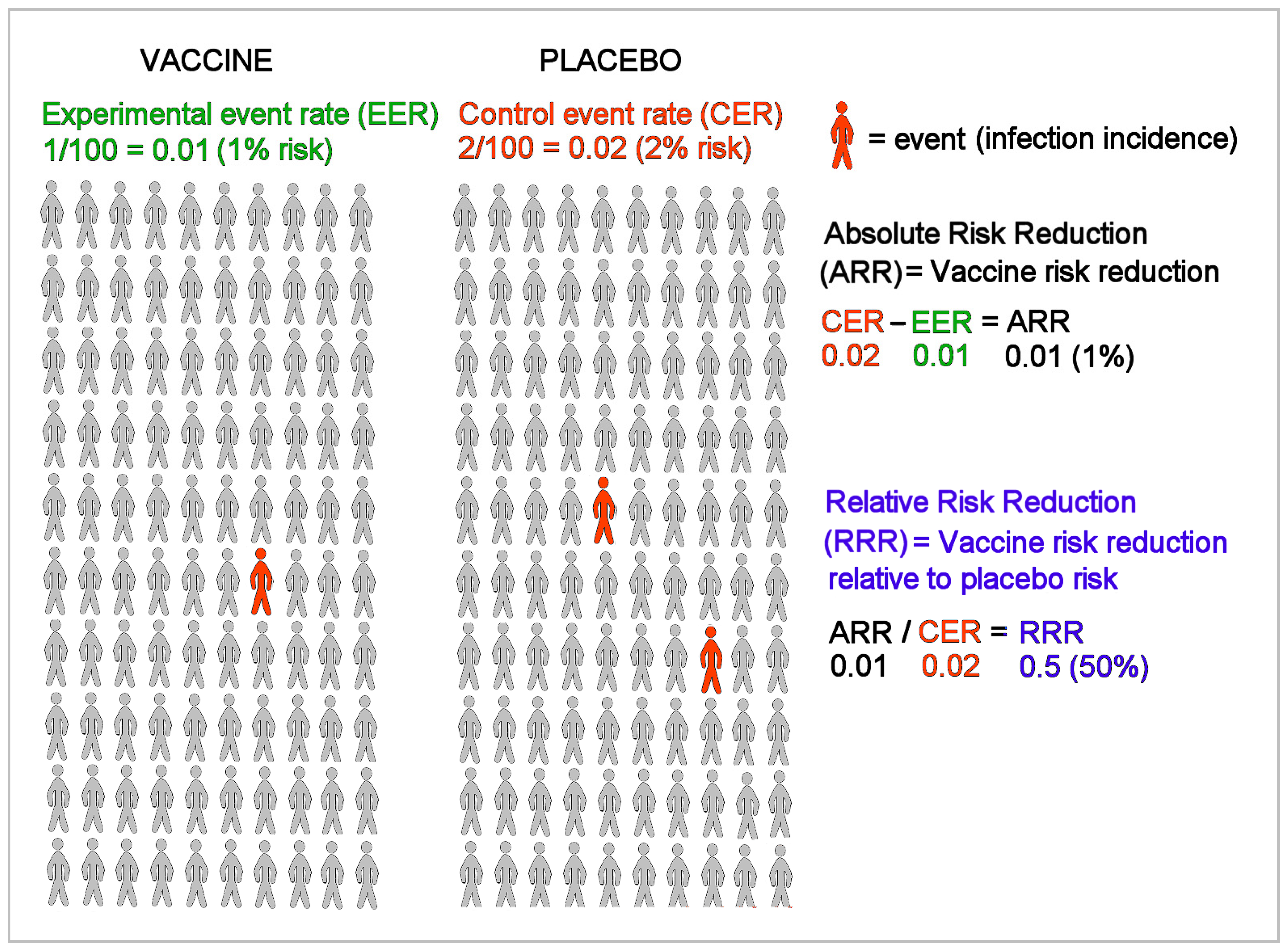



Medicina Free Full Text Outcome Reporting Bias In Covid 19 Mrna Vaccine Clinical Trials Html



Plos Medicine The Association Between Circulating 25 Hydroxyvitamin D Metabolites And Type 2 Diabetes In European Populations A Meta Analysis And Mendelian Randomisation Analysis
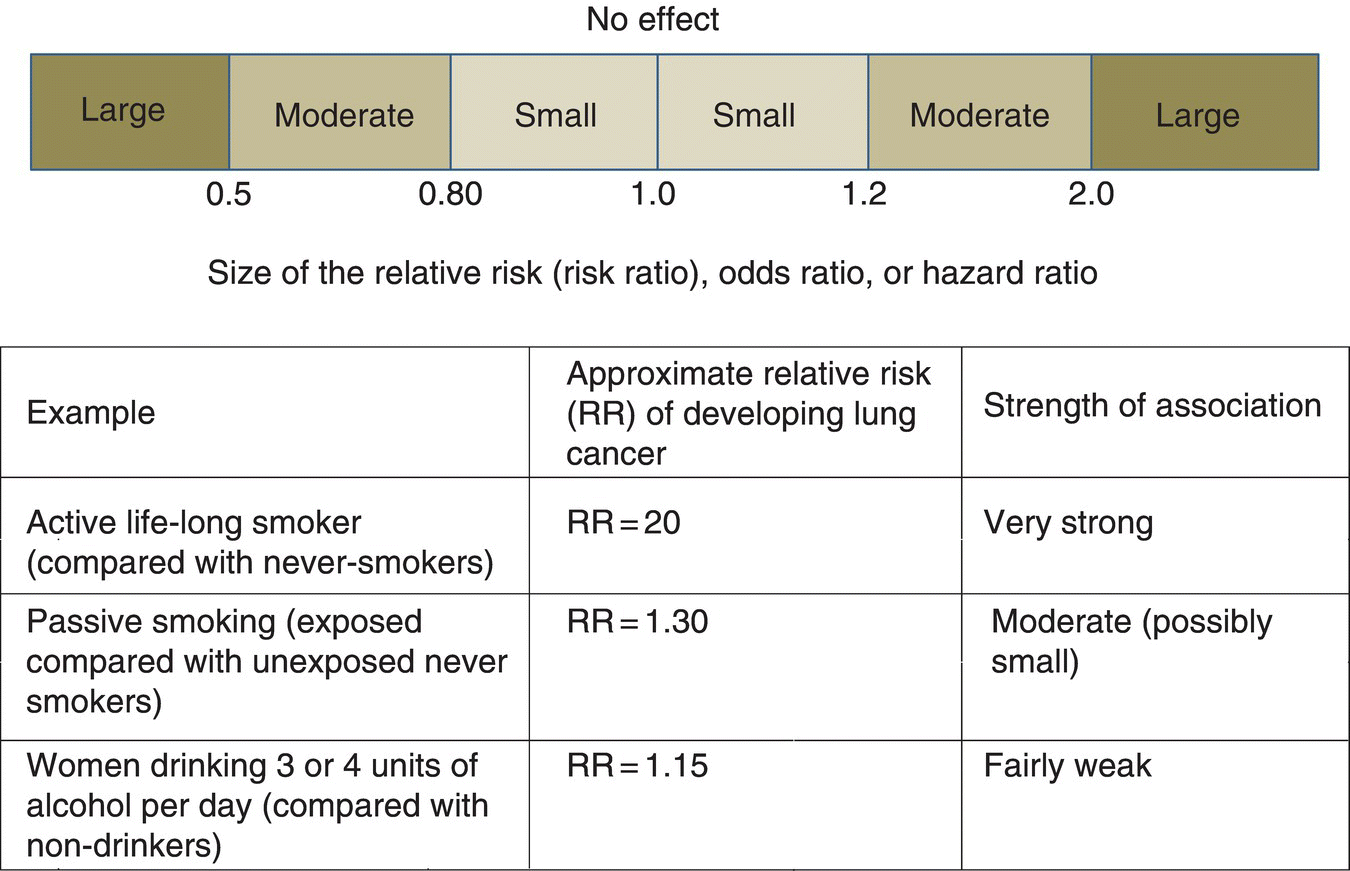



Effect Sizes Basicmedical Key



Www Jstor Org Stable
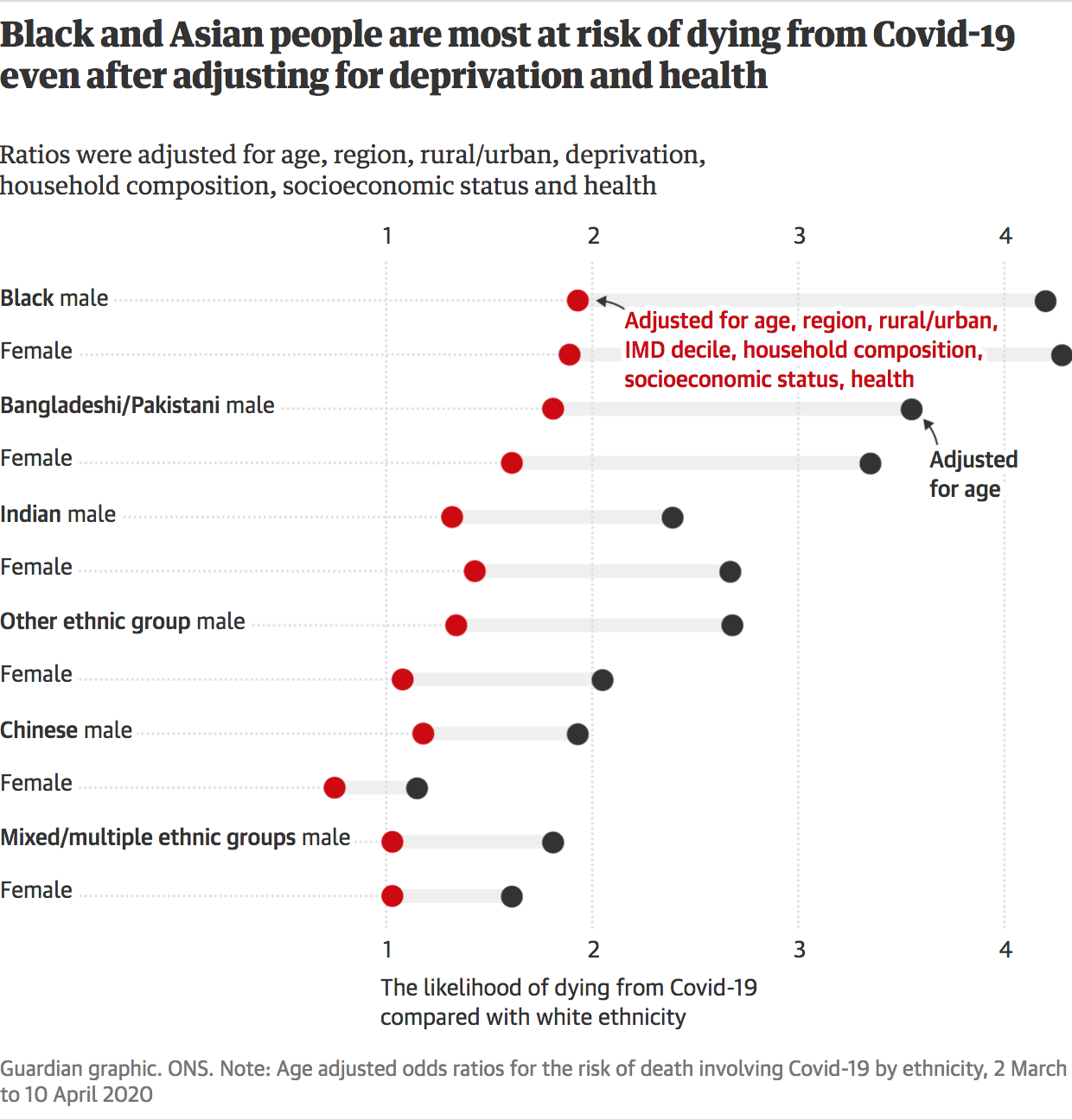



Against All Odds How To Visualise Odds Ratios To Non Expert Audiences Henry Lau
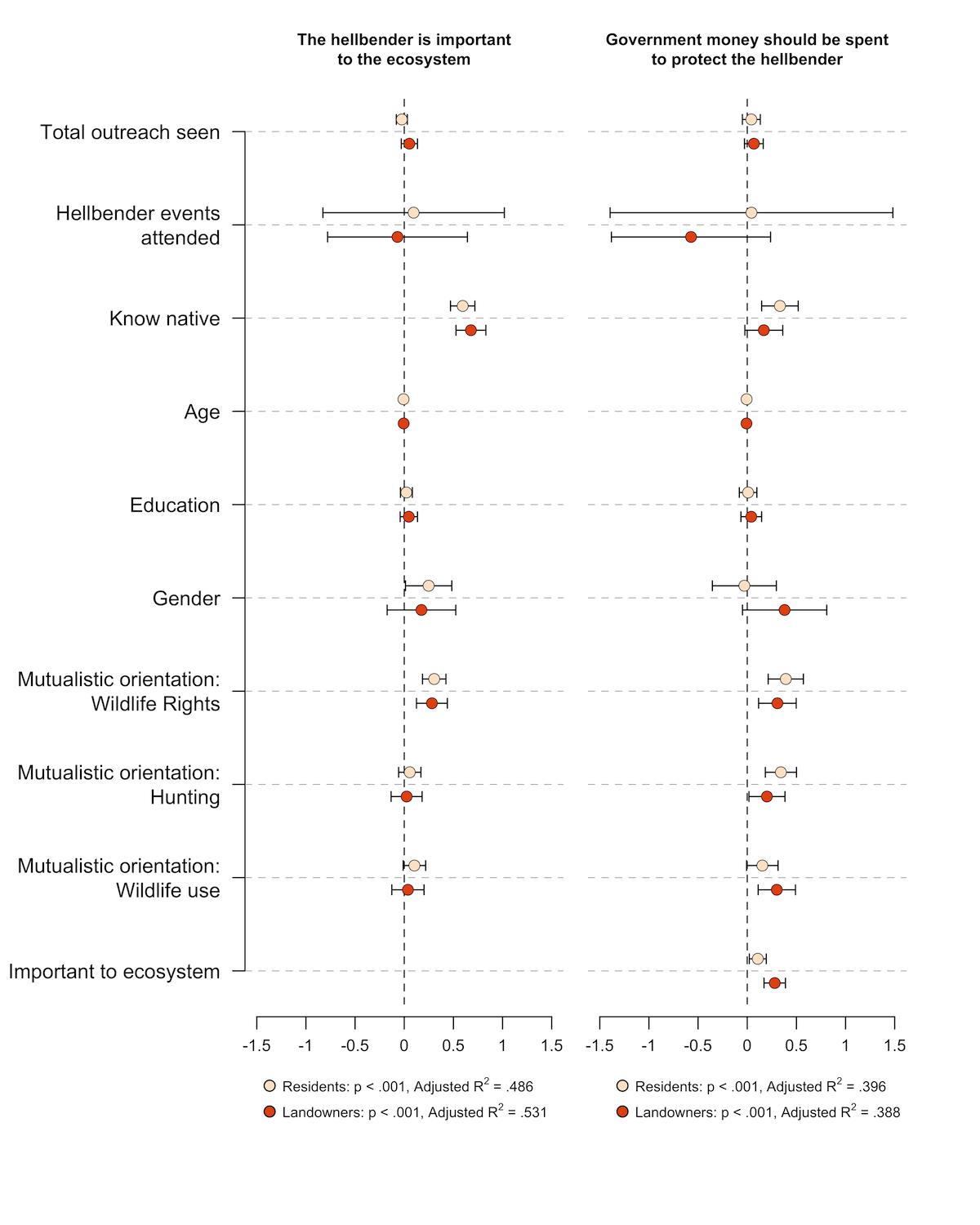



Visualizing Odds Ratios J Stuart Carlton
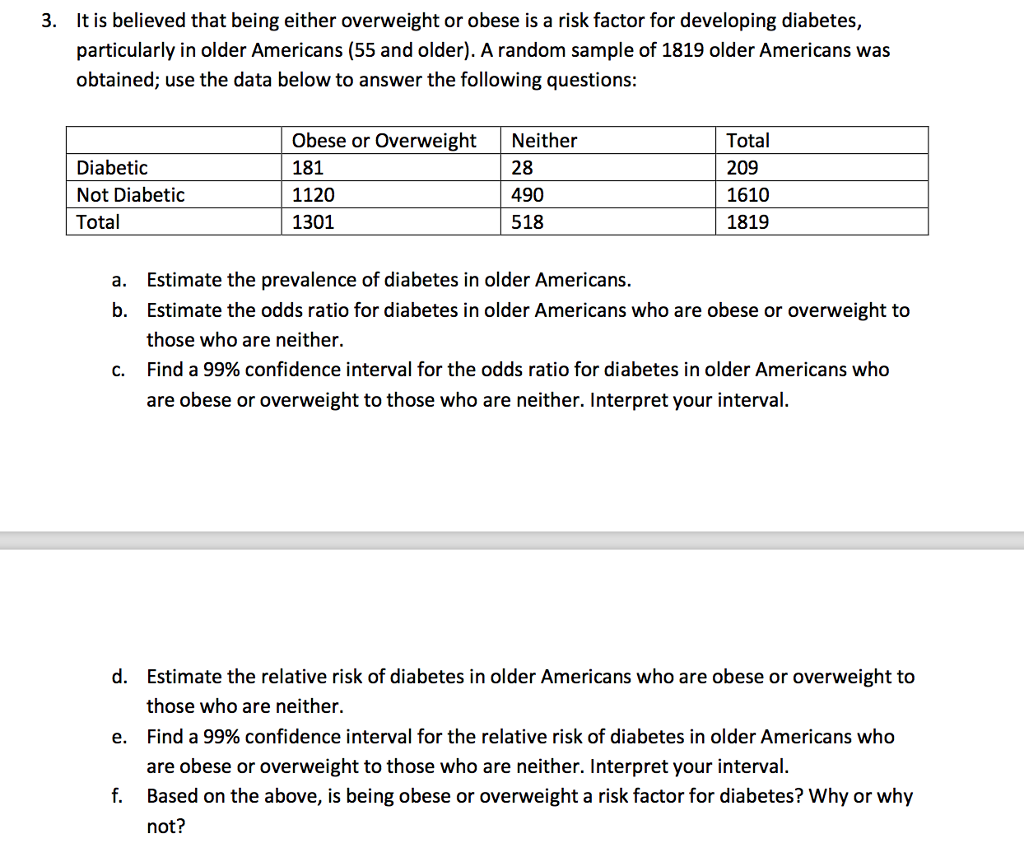



It Is Believed That Being Either Overweight Or Obe Chegg Com
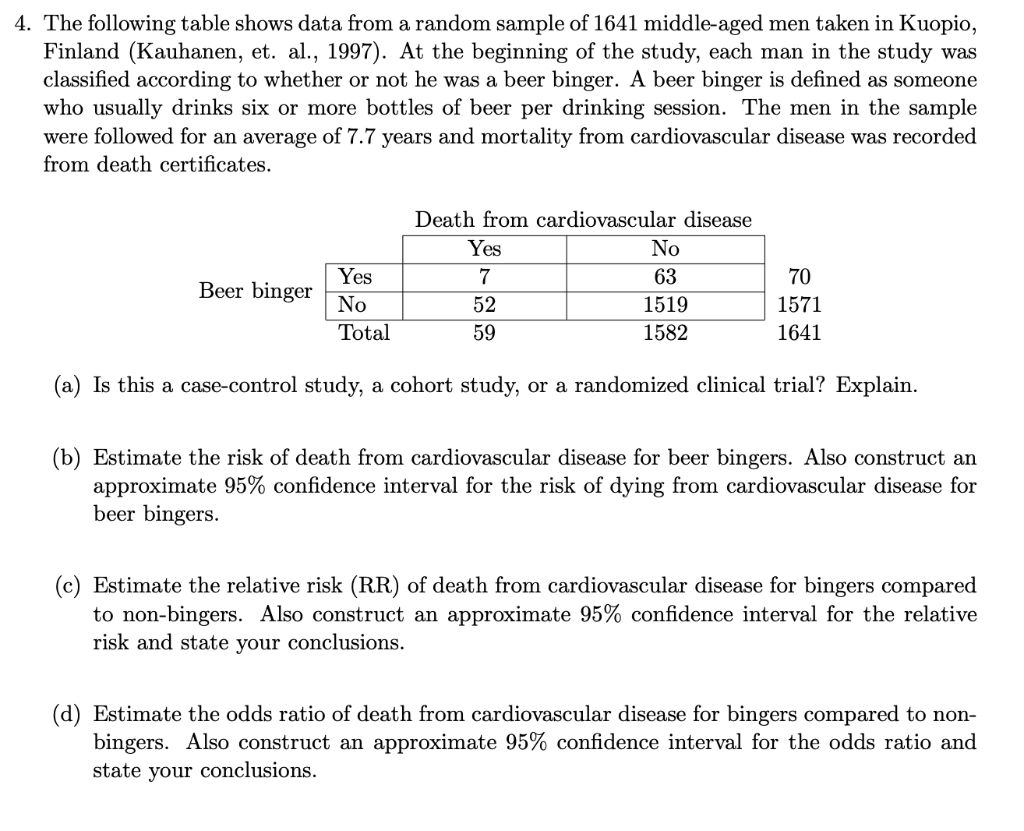



4 The Following Table Shows Data From A Random Sa Chegg Com



Http Www Floppybunny Org Robin Web Virtualclassroom Stats Basics Part13 Risks Rates Odds Pdf



Phdres Caregate Net Conferences Ay 13 14 ppt presentations Statistics 102 Pdf




How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology




Converting An Odds Ratio To A Range Of Plausible Relative Risks For Better Communication Of Research Findings The Bmj




Diagnostic Odds Ratio Wikipedia



Epidemiology Knowledge Amboss




Relative Risk Or Odds Ratio And 95 Confidence Intervals For Download Scientific Diagram




How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology




Understanding Systematic Reviews And Meta Analysis Archives Of Disease In Childhood



Http Www Ichpnet Org Resources Events Am09 Handouts 09 037 Pdf




Relative Risk 978 613 0 8



Statistic Definitions Basic Science Orthobullets



Http People Stat Sc Edu Hansont Stat5 Lecture19 Pdf




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios
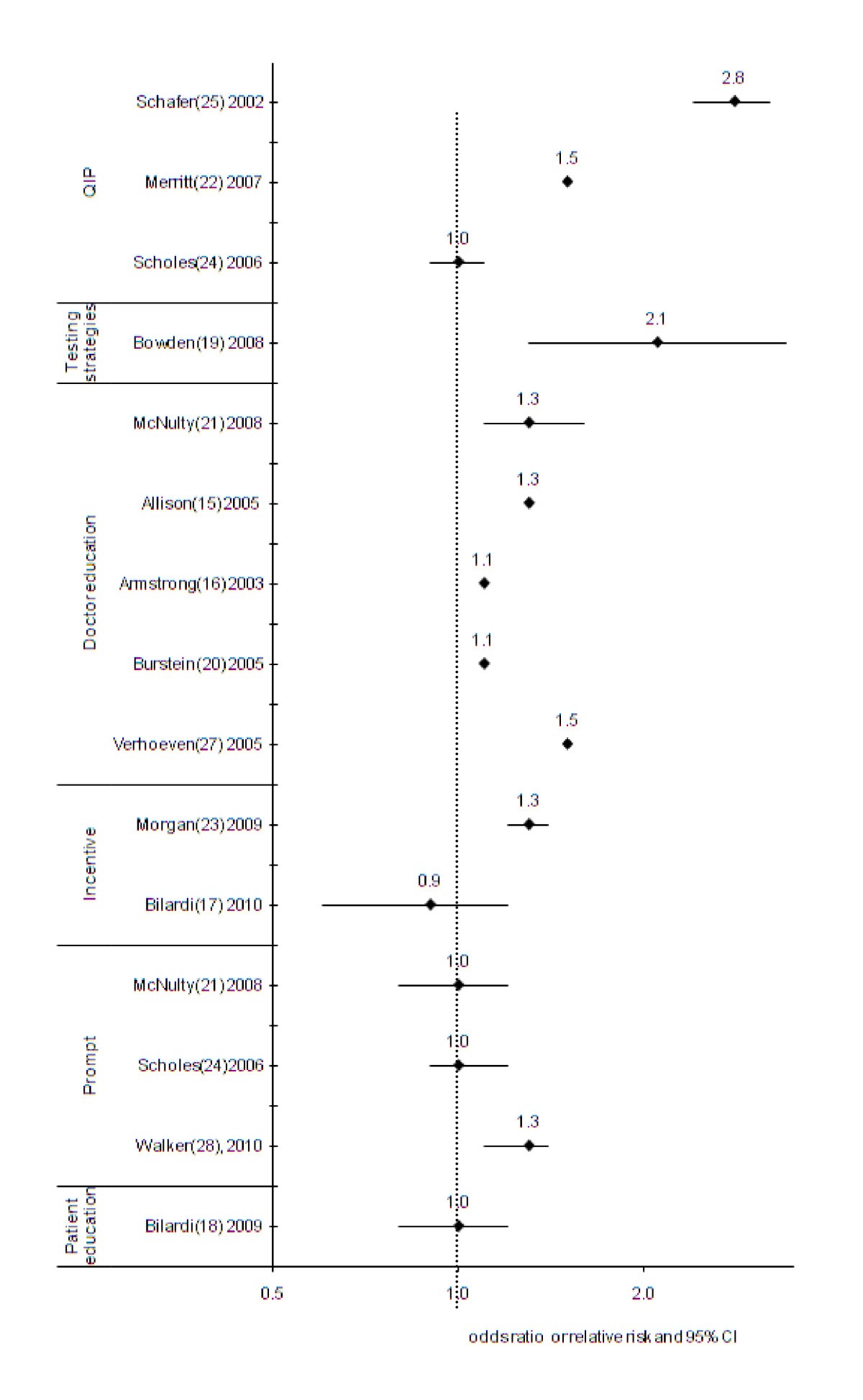



Efficacy Of Interventions To Increase The Uptake Of Chlamydia Screening In Primary Care A Systematic Review Bmc Infectious Diseases Full Text




Tutorial About Hazard Ratios Students 4 Best Evidence



Icare An R Package To Build Validate And Apply Absolute Risk Models



Www Jstor Org Stable



Plos One Bleeding Risk With Long Term Low Dose Aspirin A Systematic Review Of Observational Studies



2




Empirical Confidence Interval Calibration For Population Level Effect Estimation Studies In Observational Healthcare Data Pnas
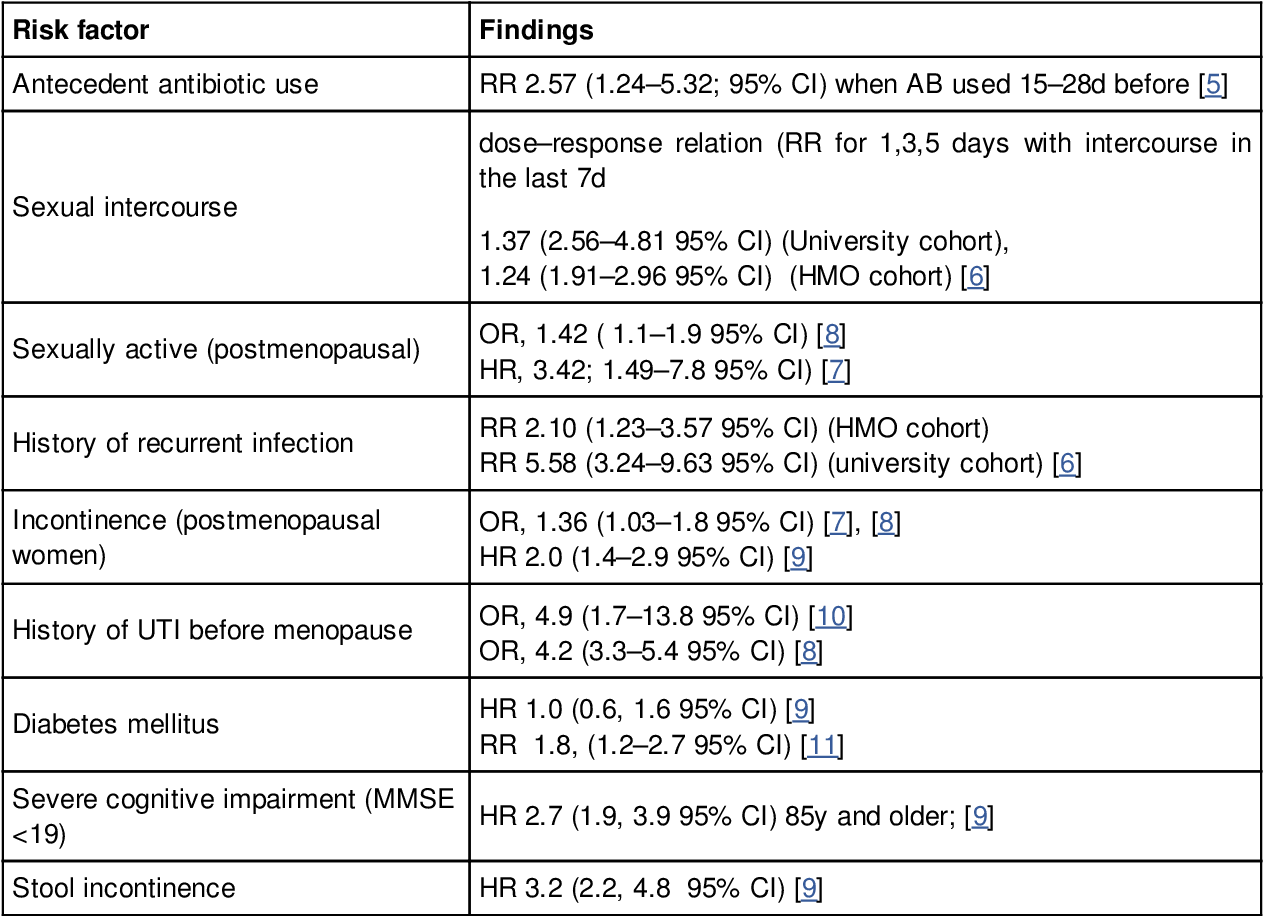



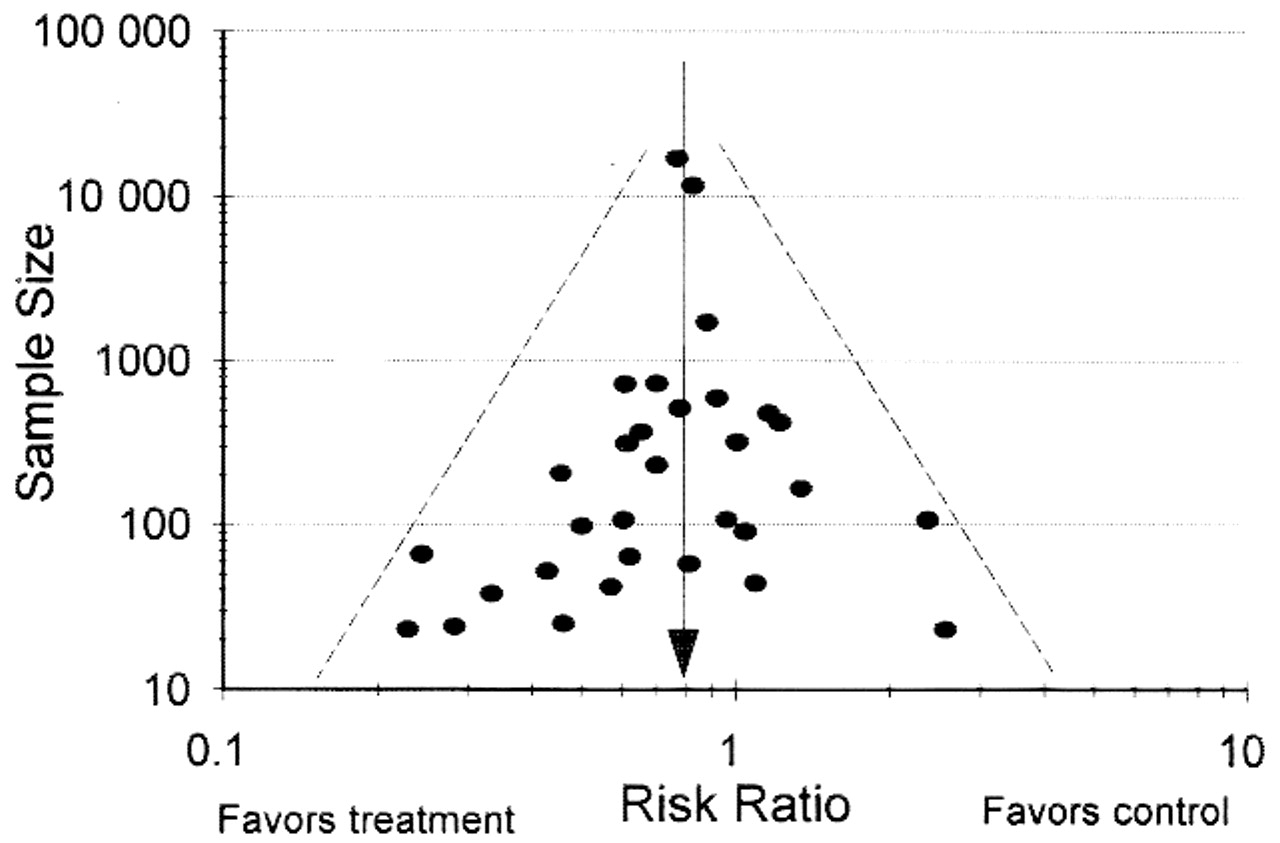
Table 1 From Diagnosis Of Uncomplicated Cystitis Uc Semantic Scholar
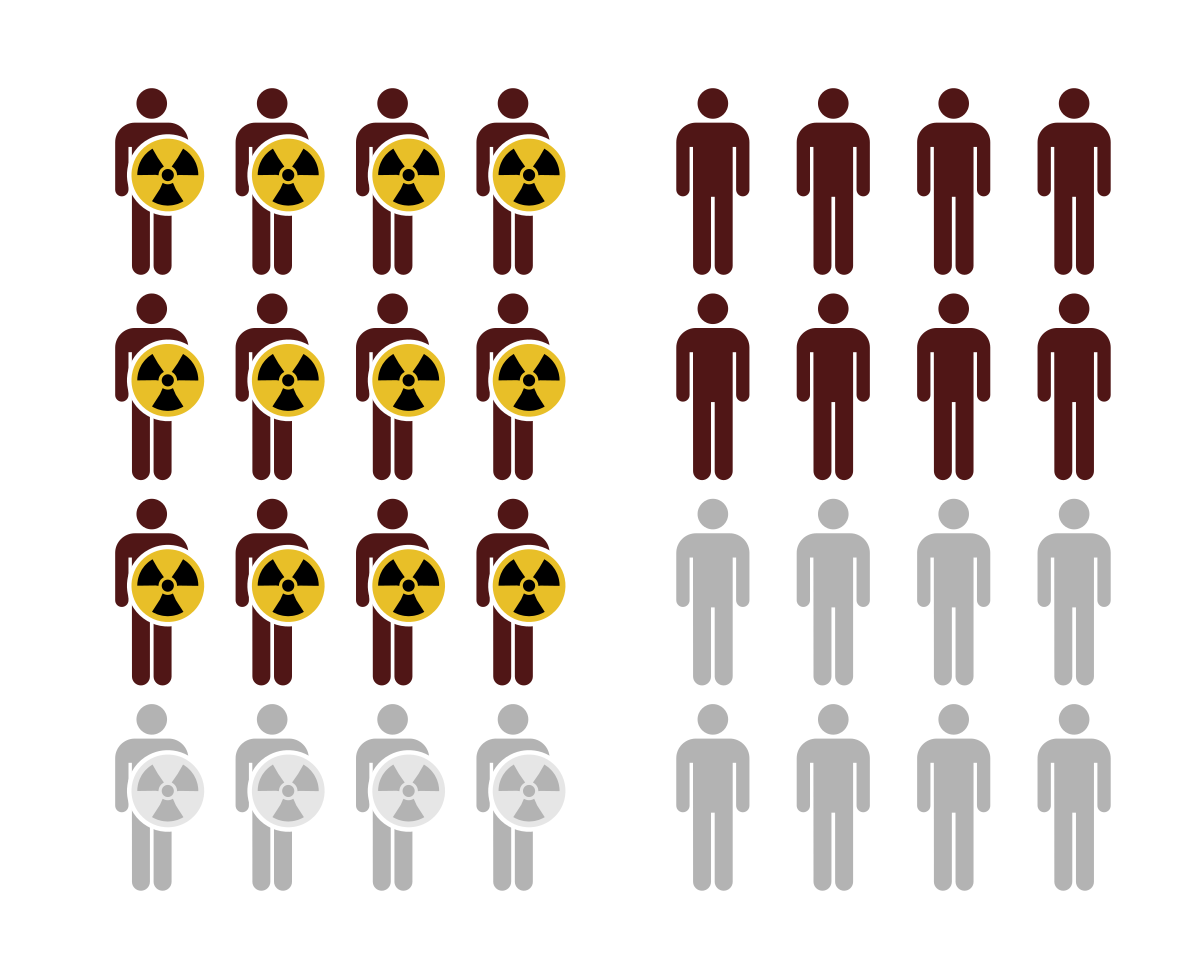



Number Needed To Harm Wikipedia




Odds Ratios The Odd One Out Stats By Slough




What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal



Beaumont Cloud Cme Com Launchscorm Aspx Caseid 112 Userid 0 Video True




Confidence Interval For An Odds Ratio




Interpreting Hazard Ratios Youtube




Review Of Alternative Approaches To Calculation Of A Confidence Interval For The Odds Ratio Of A 2 2 Contingency Table Ruxton 13 Methods In Ecology And Evolution Wiley Online Library




Biostatisticssummarypage
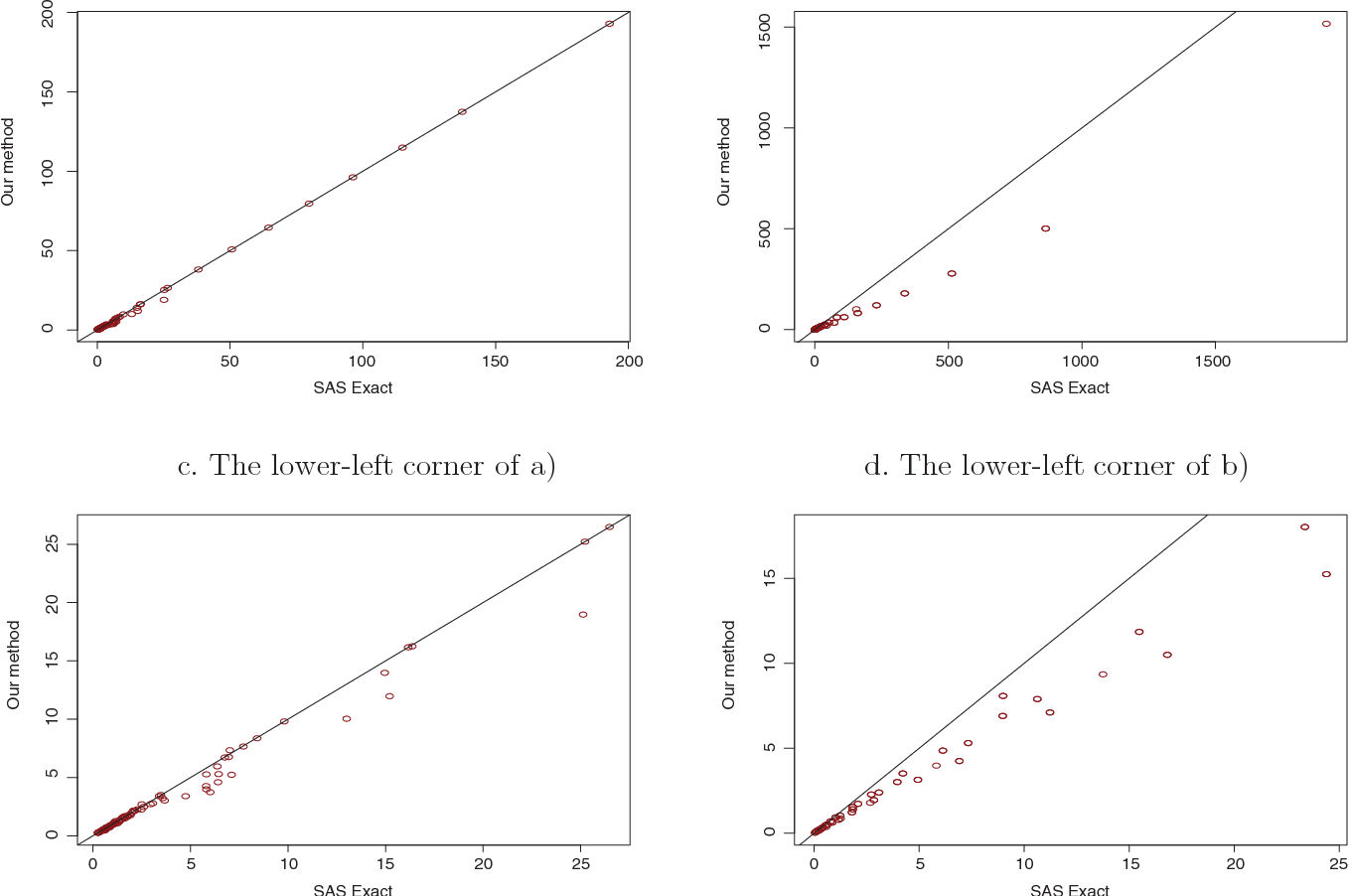



Pdf Exact Confidence Intervals For The Relative Risk And The Odds Ratio Semantic Scholar




Tutorial About Hazard Ratios Students 4 Best Evidence




Questionable Utility Of The Relative Risk In Clinical Research A Call For Change To Practice Journal Of Clinical Epidemiology




Calculate Relative Risk With 95 Confidence Intervals



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿